Surrogacy: A Boon for Infertile Couples
Infertility rates have indeed been on the rise in recent years, and a myriad of factors contribute to this trend. Lifestyle choices, late marriage, and career priorities are among the leading causes. In the modern era, where individuals are focusing more on their careers and delaying marriage and starting families, there’s a natural consequence of increased infertility cases. Late marriages are becoming more common due to various reasons, such as pursuing higher education, establishing careers, and financial stability. However, as individuals age, especially women, fertility declines, making it more challenging to conceive naturally says the experts of Best Surrogacy Centre in Manikonda. Additionally, lifestyle choices like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of exercise can further exacerbate fertility issues. Fortunately, advancements in medical technology have led to the development of various Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART), offering hope to couples struggling with infertility. Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), and surrogacy are some of the most notable techniques that have revolutionized the field of reproductive medicine. IUI involves placing male gametes directly into the uterus during ovulation, increasing the chances of fertilization. IVF, on the other hand, involves fertilizing an egg with male gametes outside the body and then implanting the embryo into the uterus. Both IUI and IVF have helped many couples achieve successful pregnancies when traditional methods have failed.
Best Surrogacy Clinic in Manikonda
Surrogacy, in particular, has emerged as a significant solution for couples who cannot conceive or carry a pregnancy to term due to medical reasons. In surrogacy at Best Surrogacy Clinic in Manikonda, a woman carries and delivers a child for another individual or couple, allowing them to experience parenthood despite their own fertility challenges. This method has been particularly beneficial for women who may have medical conditions that prevent them from carrying a pregnancy, or for same-sex male couples who wish to have biological children. These assisted reproductive technologies have provided a ray of hope for countless couples worldwide, enabling them to fulfill their dreams of starting a family. While the rise in infertility rates may present challenges, the advancements in medical science offer promising solutions and opportunities for those facing difficulties in conceiving naturally.
What is Surrogacy
Surrogacy is an arrangement where a woman (surrogate mother) agrees to carry and give birth to a child for the intended parent(s) who will raise the child. It involves the surrogate mother becoming pregnant through assisted reproductive technology, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI), using either the intended parent’s genetic material or donated eggs and/or male gametes.
There are two main types of Surrogacy in Manikonda:
- Traditional Surrogacy (Partial or Straight Surrogacy):
In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate mother is artificially inseminated with the intended father’s male gametes, making her both the genetic and gestational mother of the child. This type of surrogacy is less common nowadays due to the potential legal complications surrounding the surrogate’s parental rights.
- Gestational Surrogacy (Host or Full Surrogacy):
Gestational surrogacy is the more prevalent form of surrogacy today. In this arrangement, the surrogate mother has no genetic link to the child she carries. The intended parents’ egg and male gametes, or donor egg and/or male gametes, are used to create an embryo through IVF. The embryo is then transferred to the surrogate mother’s uterus, where she will carry and give birth to the child. Since the surrogate mother has no genetic connection to the child, the intended parents are considered the legal parents from the moment of conception.
Within gestational surrogacy, there are different types based on the genetic material used:
- Traditional Gestational Surrogacy: The intended mother’s egg and the intended father’s male gametes are used to create the embryo.
- Egg Donation Gestational Surrogacy: A donor egg is used, fertilized with the intended father’s male gametes, and the embryo is transferred to the surrogate mother.
- Male gametes Donation Gestational Surrogacy: The intended mother’s egg is fertilized with donor male gametes, and the embryo is transferred to the surrogate mother.
- Double Donation Gestational Surrogacy: Both the egg and male gametes are donated, and the embryo is transferred to the surrogate mother.
Surrogacy can be further categorized as commercial surrogacy, where the surrogate mother is compensated for her services, or altruistic surrogacy, where the surrogate mother receives no financial compensation beyond reimbursement for medical and related expenses.
The legal and ethical considerations surrounding surrogacy vary greatly across different countries and jurisdictions, with some places allowing and regulating it, while others prohibit or restrict certain forms of surrogacy.
When surrogacy is a viable option
Surrogacy becomes a viable option for individuals or couples who are unable to conceive or carry a pregnancy due to various reasons. Here are some common scenarios where people may consider surrogacy:
- Medical Conditions:
- Infertility: Couples who are unable to conceive naturally due to infertility issues, such as ovulation disorders, endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes, or male factor infertility (low male gametes count, poor male gametes motility, or abnormal male gametes morphology), may opt for surrogacy.
- Uterine Complications: Women who have had a hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) or those born without a uterus (congenital uterine abnormalities like Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome) may consider surrogacy as a path to parenthood.
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Couples who have experienced multiple miscarriages or stillbirths due to underlying medical conditions may turn to surrogacy to increase their chances of having a successful pregnancy.
- Health Risks: Women with certain medical conditions, such as severe heart disease, kidney disease, or cancer, where pregnancy could pose a significant risk to their health, may consider surrogacy as a safer alternative.
- Same-Sex Couples:
- Male Same-Sex Couples: In the case of male same-sex couples, surrogacy provides an opportunity for them to have a child genetically related to one or both partners. They may use their own male gametes (male gametes) or donated male gametes, combined with a donated egg, and engage a gestational surrogate to carry the pregnancy.
- Female Same-Sex Couples: For female same-sex couples, surrogacy allows them to have a child genetically related to one or both partners. One partner’s egg can be fertilized with donated male gametes, and the resulting embryo can be transferred to a gestational surrogate.
- Single Individuals:
- Single Men: Single men who wish to have a child may choose surrogacy as a path to parenthood. They can use their own male gametes or donated male gametes, combined with a donated egg, and engage a gestational surrogate to carry the pregnancy.
- Single Women: Single women who are unable to carry a pregnancy due to medical reasons or personal preferences may opt for surrogacy. They can use their own egg, fertilized with donated male gametes, and have a gestational surrogate carry the pregnancy.
- Family Building for Intended Parents:
- Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD): Couples who are at risk of passing on genetic disorders or have a history of genetic conditions in their families may choose to undergo PGD, where embryos are screened for specific genetic conditions before being transferred to a gestational surrogate.
- Advanced Maternal Age: As women age, the risk of complications during pregnancy increases. Older women who wish to have a child may consider surrogacy as a safer option.
- Personal or Cultural Reasons:
In some cases, individuals or couples may choose surrogacy for personal or cultural reasons, such as fear of pregnancy or childbirth, or to avoid potential genetic disorders or disabilities.
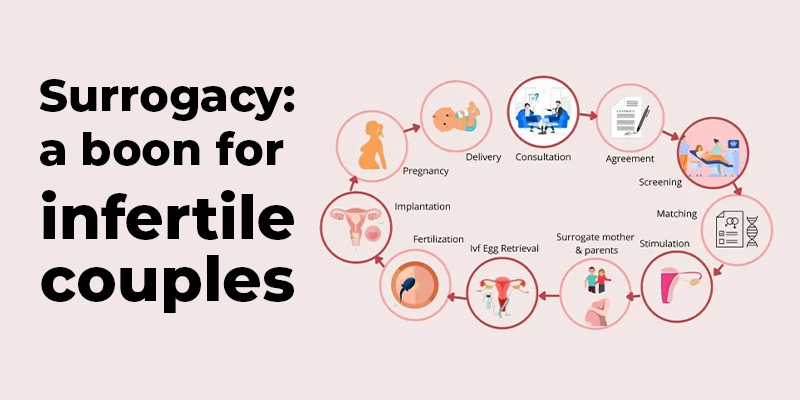
Steps in surrogacy
Surrogacy is a complex process that involves multiple steps and careful planning. Here are the detailed steps typically involved in the surrogacy journey:
- Initial Consultation and Evaluation:
– Intended parents and potential surrogate mothers undergo medical and psychological evaluations to determine their eligibility for surrogacy.
– Legal consultations are conducted to understand the laws and regulations surrounding surrogacy in the respective jurisdiction.
– Counseling sessions are undertaken to ensure that all parties are emotionally prepared for the surrogacy process.
- Finding a Surrogate Mother or Intended Parents:
– Intended parents may work with surrogacy agencies or fertility clinics to find a suitable surrogate mother who meets their criteria.
– Surrogate mothers may also independently seek out intended parents through various channels or platforms.
– Background checks, medical histories, and compatibility assessments are conducted to match intended parents and surrogate mothers.
- Legal Contracts and Agreements:
– Comprehensive legal agreements are drafted and reviewed by attorneys representing all parties involved.
– These contracts outline the rights, responsibilities, and expectations of the intended parents and surrogate mother.
– Issues such as compensation, medical expenses, legal parentage, and potential termination of the agreement are addressed.
- Fertility Treatments and Embryo Creation:
– Intended parents or donors undergo the necessary medical procedures to retrieve eggs and male gametes (male gametes).
– In vitro fertilization (IVF) is performed to create embryos using the intended parents’ or donors’ genetic material.
– Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) may be performed to screen for genetic disorders or select for specific traits.
- Embryo Transfer and Pregnancy:
– The surrogate mother undergoes medical preparations, including hormonal treatments and synchronization of her cycle.
– One or more embryos are transferred to the surrogate mother’s uterus through a procedure similar to IVF.
– If the transfer is successful, the surrogate mother will carry the pregnancy until delivery.
- Prenatal Care and Support:
– The surrogate mother receives regular prenatal care and medical monitoring throughout the pregnancy.
– Intended parents and the surrogate mother maintain open communication and support each other during this time.
– Counseling and emotional support may be provided to all parties to navigate the emotional aspects of the surrogacy journey.
- Birth and Parental Rights Establishment:
– The surrogate mother gives birth to the child or children in a hospital or birthing center.
– Depending on the jurisdiction and legal agreements, steps may be taken to establish the intended parents’ legal parentage, such as obtaining a pre-birth order or post-birth adoption.
– The surrogate mother relinquishes her parental rights, and the intended parents assume full legal custody of the child.
- Post-Birth Transition and Support:
– The intended parents welcome their newborn child or children into their family.
– Counseling and support services may be provided to help the intended parents, surrogate mother, and any other children involved adjust to the new family dynamic.
– Ongoing communication and relationships between the parties may be maintained, depending on their preferences and agreements.
Steps and requirements for surrogacy can vary significantly depending on the location, laws, and regulations in place. Additionally, the emotional and psychological aspects of surrogacy are significant, and all parties involved should receive appropriate counseling and support throughout the process.
Advantages of surrogacy
Surrogacy offers several advantages for individuals or couples seeking to build a family. Here are some of the key advantages of surrogacy, discussed in detail:
- Provides a Path to Parenthood for Intended Parents:
– Surrogacy offers a viable option for individuals or couples who are unable to conceive or carry a pregnancy themselves due to various medical reasons, such as infertility, uterine complications, recurrent pregnancy loss, or health risks associated with pregnancy.
– It allows intended parents to have a child genetically related to one or both of them, fulfilling their desire for a biologically connected family.
– For same-sex couples or single individuals, surrogacy provides an opportunity to become parents and experience the joy of raising a child.
- Increased Success Rates:
– Advances in assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and preimplantation genetic testing (PGT), have significantly improved the success rates of surrogacy arrangements.
– By utilizing a healthy surrogate mother who is carefully screened and monitored, the chances of a successful pregnancy and delivery are often higher compared to traditional conception methods for intended parents with fertility challenges.
– PGT allows for the selection of genetically viable embryos, reducing the risk of certain genetic disorders and increasing the chances of a healthy pregnancy and child.
- 3. Reduced Health Risks for Intended Mothers:
– For intended mothers with medical conditions that could make pregnancy risky or life-threatening, surrogacy provides a safer alternative to carry a child without endangering their own health.
– Conditions such as severe heart disease, kidney disease, cancer, or other high-risk medical conditions may preclude intended mothers from safely carrying a pregnancy themselves.
– Surrogacy allows these intended mothers to have a child while minimizing potential complications and risks associated with pregnancy and childbirth.
- Emotional and Psychological Benefits:
– Surrogacy can alleviate the emotional distress and psychological burden associated with infertility or the inability to carry a pregnancy for intended parents.
– It offers a sense of hope and the possibility of fulfilling the dream of parenthood, which can have a profound positive impact on the intended parents’ emotional well-being.
– For surrogate mothers, the experience of helping others create a family can be deeply rewarding and provide a sense of personal fulfillment.
- Legal and Financial Considerations:
– In certain jurisdictions, surrogacy arrangements are legally recognized and regulated, providing a clear framework for establishing parentage and ensuring the rights and responsibilities of all parties involved.
– Commercial surrogacy can provide financial compensation for surrogate mothers, which may serve as an incentive and help cover expenses related to the surrogacy process.
– Legal contracts and agreements help to protect the interests of all parties involved and establish clear expectations and responsibilities.
- Flexibility and Control:
– Surrogacy allows intended parents to have greater control over the gestational environment and prenatal care compared to traditional adoption processes.
– Intended parents can be involved in the selection of the surrogate mother, taking into account factors such as lifestyle, medical history, and compatibility.
– Surrogate mothers often follow specific guidelines and receive close medical monitoring during the pregnancy, ensuring the best possible outcome for the intended child.
while surrogacy offers several advantages, it is a complex and emotionally challenging process that requires careful consideration, legal guidance, and professional support. The decision to pursue surrogacy should be made after thorough research, counseling, and careful weighing of the ethical, legal, and emotional implications involved.
FAQ
- What is surrogacy, and how does it work?
Surrogacy is a process where a woman, known as the surrogate or gestational carrier, carries a child for intended parents who are unable to conceive or carry a pregnancy to term. There are two main types: traditional surrogacy, where the surrogate’s own egg is fertilized with the intended father’s male gametes through artificial insemination, and gestational surrogacy, where the embryo is created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) using either the intended parents’ genetic material or donated gametes and then implanted into the surrogate’s uterus.
- What are the reasons people choose surrogacy?
People may choose surrogacy for various reasons, including infertility, medical conditions that make pregnancy unsafe, or same-sex couples and single individuals who wish to have biological children. Surrogacy offers a solution for those who are unable to carry a pregnancy themselves but still want to have a genetic connection to their child.
- How are surrogates selected, and what are the criteria?
Surrogates undergo a rigorous screening process to ensure they are physically and emotionally capable of carrying a pregnancy to term. Criteria often include age (typically between 21 and 40), previous successful pregnancies, good physical health, stable mental health, and a supportive home environment. Surrogates must also undergo medical and psychological evaluations before being matched with intended parents.
- What legal considerations are involved in surrogacy arrangements?
Surrogacy laws vary greatly by country and even by state or region within countries. It’s crucial for all parties involved to understand and comply with the legal requirements governing surrogacy in their jurisdiction. Legal agreements outlining parental rights, financial arrangements, and the surrogate’s obligations are typically drafted before any medical procedures take place to protect all parties involved.
- What are the emotional challenges faced by surrogates and intended parents?
Surrogacy can be emotionally complex for all parties involved. Surrogates may experience attachment to the baby they carry, even though they have no genetic connection. Intended parents may struggle with feelings of anxiety, guilt, or uncertainty about entrusting another person with such a significant role in their journey to parenthood. Open communication, counseling, and support throughout the process are essential for addressing these emotional challenges.
- 6. How do financial aspects work in surrogacy arrangements?
Surrogacy can be financially significant for all parties involved. Intended parents typically cover the costs associated with the surrogate’s medical expenses, legal fees, compensation for her time and effort, and other related expenses such as maternity clothing and travel. The specifics of financial arrangements vary depending on the agreed-upon terms outlined in the surrogacy contract.
- What are the medical procedures involved in gestational surrogacy?
In gestational surrogacy, the process begins with the creation of embryos through IVF using the intended parents’ or donated gametes. Once the embryos are ready, they are transferred to the surrogate’s uterus, where they implant and hopefully result in a successful pregnancy. Surrogates may need to undergo hormone treatments to prepare their uterus for embryo implantation and support early pregnancy.