Everything You Should Know About The Best IVF Center In Secunderabad
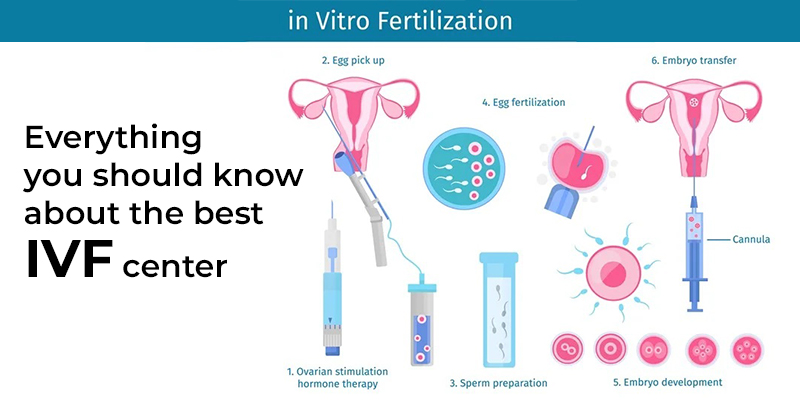
Infertility is indeed a challenging and emotional issue that many couples face. In vitro fertilization (IVF) has emerged as a significant advancement in reproductive technology and has provided hope and solutions for couples struggling with infertility. IVF at the best IVF center in Secunderabad involves fertilizing an egg with sperm outside the body and then implanting the fertilized embryo into the uterus.
Best IVF center Near me
IVF stands for “in vitro fertilization.” It is a complicated set of treatments that can help a woman get pregnant. For most couples, infertility means they have tried to get pregnant for at least a year and still haven’t been able to. IVF can also be used to keep DNA problems from being passed on to a child. During in vitro development at the best IVF center near me, sperm is brought into a lab and developed eggs are taken from ovaries. Then, one or more of the fertilized eggs are put into the uterus through a process. The whole IVF process takes two to three weeks. Sometimes these steps are split into different parts and the process can take longer.
Best IVF center Near me Secunderabad
In vitro fertilization at the Best IVF center Near me, Secunderabad is the best way to treat infertility which includes working with eggs or embryos and sperm. Assisted reproductive technology is the name for all of these methods put together.
In vitro fertilization is a way to fix DNA problems or infertility. You and your partner might be able to try other treatments for infertility before going through with IVF.
If you are over 40 and can’t have children, IVF is sometimes the main treatment you can get. You can also do it if you have certain health problems. For instance, you or your partner may be able to use IVF if you or they have:
- Damage to or closure of the fallopian tube. The fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. It is hard for an egg to be fertilized or for a baby to get to the uterus if both tubes are broken or stopped.
- Problems with ovulation. If ovulation doesn’t happen or doesn’t happen often, there aren’t as many eggs for sperm to fertilize.
- Having endometriosis. When tissue that looks like the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus, this disease can happen. With endometriosis, the ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes are many times affected.
- Uterine bumps. The uterus has growths called fibroids. A lot of the time, they’re not cancer. People in their 30s and 40s often have them. Fibroids can cause a fertilized egg to have trouble attaching to the lining of the uterus.
- Surgery in the past to avoid getting pregnant. The fallopian tubes are cut or closed during a procedure called tubal closure to stop pregnancy for good. IVF might help you get pregnant after having your tubes tied. People who don’t want or can’t have surgery to undo tubal ligation might be able to do this instead.
- Some problems with sperm. A lack of sperm or strange changes in how they move, grow, or form can make it hard for sperm to fertilize an egg. If medical tests find issues with sperm, a visit to an infertility specialist might be needed to see if there are treatable problems or other health concerns.
- Unknown reasons for infertility. This is what happens when tests can’t figure out why someone can’t have children.
- A disease caused by genes. Your healthcare team may suggest that you get an IVF treatment if you or your partner are likely to pass on a genetic problem to your child. It’s called genetic testing before pregnancy. The eggs are checked for genetic problems after they have been laid and fertilized. Still, you can’t find all of these illnesses. Embryos that don’t seem to have a genetic problem can be put into the uterus.
- A desire to maintain pregnancy due to cancer or other health problems. Radiation and medication used to treat cancer can make it harder to get pregnant. If you’re about to start treatment for cancer, IVF could be a way to still have a baby in the future. Eggs can be removed from their eggs and saved for later use. Or the eggs can be fertilized and saved as embryos for future use.
Women who don’t have a working uterus or for whom pregnancy poses a serious health risk might choose IVF using another person to carry the pregnancy. The person is called a gestational carrier. In this case, your eggs are fertilized with sperm, but the embryos that result are placed in the gestational carrier’s uterus.
How you prepare
To get started, you’ll want to find a reputable fertility clinic. A fertility clinic’s success rate depends on many things. These include the ages and medical issues of people they treat, as well as the clinic’s treatment approaches. When you talk with a representative at a clinic, also ask for detailed information about the costs of each step of the procedure.
Before you start a cycle of IVF using your own eggs and sperm, you and your partner will likely need various screening tests. These include:
- Ovarian reserve testing. This involves getting blood tests to find out how many eggs are available in the body. This is also called egg supply. The results of the blood tests often used together with an ultrasound of the ovaries, can help predict how your ovaries will respond to fertility medicines.
- Semen analysis. Semen is the fluid that contains sperm. An analysis of it can check the amount of sperm, their shape and how they move. This testing may be part of an initial fertility evaluation. Or it might be done shortly before the start of an IVF treatment cycle.
- Infectious disease screening. You and your partner will both be screened for diseases such as HIV.
- Practice embryo transfer. This test doesn’t place a real embryo in the uterus. It may be done to figure out the depth of your uterus. It also helps determine the technique that’s most likely to work well when one or more actual embryos are inserted.
- Uterine exam. The inside lining of the uterus is checked before you start IVF. This might involve getting a test called son hysterography. Fluid is sent through the cervix into the uterus using a thin plastic tube. The fluid helps make more detailed ultrasound images of the uterine lining. Or the uterine exam might include a test called hysteroscopy. A thin, flexible, lighted telescope is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus to see inside it.
What you can expect
After the preparations are completed, one cycle of IVF can take about 2 to 3 weeks. More than one cycle may be needed. The steps in a cycle go as follows:
Treatment to make mature eggs
The start of IVF cycle begins by using lab-made hormones to help the ovaries to make eggs — rather than the single egg that usually develops each month. Multiple eggs are needed because some eggs won’t fertilize or develop correctly after they’re combined with sperm.
Certain medicines may be used to:
- Stimulate the ovaries. You might receive shots of hormones that help more than one egg develop at a time. The shot may contain a follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), a luteinizing hormone (LH) or both.
- Help eggs mature. A hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), or other medicines, can help the eggs ripen and get ready to be released from their sacs, called follicles, in the ovaries.
- Delay ovulation. These medicines prevent the body from releasing the developing eggs too soon.
- Prepare the lining of the uterus. You might start to take supplements of the hormone progesterone on the day of the procedure to collect your eggs. Or you might take these supplements around the time an embryo is placed in the uterus. They improve the odds that a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of your uterus.
Your doctor decides which medicines to use and when to use them.
Most often, you’ll need 1 to 2 weeks of ovarian stimulation before your eggs are ready to be collected with the egg retrieval procedure. To figure out when the eggs are ready, you may need:
- Vaginal ultrasound, an imaging exam of the ovaries to track the developing follicles. Those are the fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries where eggs mature.
- Blood tests, to check on how you respond to ovarian stimulation medicines. Estrogen levels often rise as follicles develop. Progesterone levels remain low until after ovulation.
Sometimes, IVF cycles need to be canceled before the eggs are collected. Reasons for this include:
- Not enough follicles develop.
- Ovulation happens too soon.
- Too many follicles develop, raising the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
- Other medical issues happen.
If your cycle is canceled, your care team might recommend changing medicines or the amounts you take, called doses. This might lead to a better response during future IVF cycles. Or you may be advised that you need an egg donor.
Egg retrieval
This is the procedure to collect the eggs from one or both ovaries. It takes place in your doctor’s office or a clinic. The procedure is done 34 to 36 hours after the final shot of fertility medicine and before ovulation.
- Before egg retrieval, you’ll be given medicine to help you relax and keep you from feeling pain.
- An ultrasound device is placed into the vagina to find follicles. Those are the sacs in the ovaries that each contain an egg. Then a thin needle is inserted into an ultrasound guide to go through the vagina and into the follicles to collect the eggs. This process is called transvaginal ultrasound aspiration.
- If your ovaries can’t be reached through the vagina this way, an ultrasound of the stomach area may be used to guide the needle through the stomach and into the ovaries.
- The eggs are removed from the follicles through a needle connected to a suction device. Multiple eggs can be removed in about 20 minutes.
- After the procedure, you may have cramping and feelings of fullness or pressure.
- Mature eggs are placed in a liquid that helps them develop. Eggs that appear healthy and mature will be mixed with sperm to attempt to create embryos. But not all eggs are able to be fertilized with success.
Sperm retrieval
If you’re using your partner’s sperm, a semen sample needs to be collected at your doctor’s office or clinic the morning of egg retrieval. Or sperm can be collected ahead of time and frozen.
Most often, the semen sample is collected through masturbation. Other methods can be used if a person can’t ejaculate or has no sperm in the semen. For example, a procedure called testicular aspiration uses a needle or surgery to collect sperm directly from the testicle. Sperm from a donor also can be used. Sperm are separated from the semen fluid in the lab.
Fertilization
Two common methods can be used to try to fertilize eggs with sperm:
- Conventional insemination. Healthy sperm and mature eggs are mixed and kept in a controlled environment called an incubator.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). A single healthy sperm is injected right into each mature egg. Often, ICSI is used when semen quality or number is an issue. Or it might be used if fertilization attempts during prior IVF cycles didn’t work.
In certain situations, other procedures may be recommended before embryos are placed in the uterus. These include:
- Assisted hatching. About 5 to 6 days after fertilization, an embryo “hatches” from the thin layer that surrounds it, called a membrane. This lets the embryo attach to the lining of the uterus.
If you’re older and you want to get pregnant, or if you have had past IVF attempts that didn’t work, a technique called assisted hatching might be recommended. With this procedure, a hole is made in the embryo’s membrane just before the embryo is placed in the uterus. This helps the embryo hatch and attach to the lining of the uterus. Assisted hatching is also useful for eggs or embryos that were frozen, as that process can harden the membrane.
- Preimplantation genetic testing. Embryos are allowed to develop in the incubator until they reach a stage where a small sample can be removed. The sample is tested for certain genetic diseases or the correct number of threadlike structures of DNA, called chromosomes. There are usually 46 chromosomes in each cell. Embryos that don’t contain affected genes or chromosomes can be transferred to the uterus.
Preimplantation genetic testing can lower the chances that a parent will pass on a genetic problem. It can’t get rid of the risk completely. Prenatal testing may still be recommended during pregnancy.
Embryo transfer
Blastocyst Enlarge image
The procedure to place one or more embryos in the uterus is done at your doctor’s office or a clinic. It often takes place 2 to 6 days after eggs are collected.
- You might be given a mild sedative to help you relax. The procedure is often painless, but you might have mild cramping.
- A long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter is placed into the vagina, through the cervix and into the uterus.
- A syringe that contains one or more embryos in a small amount of fluid is attached to the end of the catheter.
- Using the syringe, the embryo or embryos are placed into the uterus.
If the procedure works, an embryo will attach to the lining of your uterus about 6 to 10 days after egg retrieval.
After the procedure
After the embryo transfer, you can get back to your usual daily routine. Your ovaries may still be enlarged, so vigorous activities or sex might cause discomfort. Ask your care team how long you should stay away from these.
Typical side effects include:
- Passing a small amount of clear or bloody fluid shortly after the procedure. This is due to the swabbing of the cervix before the embryo transfer.
- Breast tenderness due to high estrogen levels.
- Mild bloating.
- Mild cramping.
- Constipation.
Call your care team if you have moderate or severe pain, or heavy bleeding from the vagina after the embryo transfer.
Results
At least 12 days after egg retrieval, you get a blood test to find out whether you’re pregnant.
- If you’re pregnant, you’ll likely be referred to an obstetrician or other pregnancy specialist for prenatal care.
- If you’re not pregnant, you’ll stop taking progesterone and likely get your period within a week. Call your care team if you don’t get your period or if you have unusual bleeding. If you’d like to try another cycle of IVF, your care team might suggest steps you can take to improve your chances of getting pregnant next time.
The chances of giving birth to a healthy baby after using IVF depend on various factors, including:
- Maternal age. The younger you are, the more likely you are to get pregnant and give birth to a healthy baby using your own eggs during IVF. Often, people 40 and older are counseled to think about using donor eggs during IVF to boost the chances of success.
- Embryo status. Transfer of embryos that are more developed is linked with higher pregnancy rates compared with less-developed embryos. But not all embryos survive the development process. Talk with your care team about your specific situation.
- Reproductive history. People who’ve given birth before are more likely to be able to get pregnant using IVF than are people who’ve never given birth. Success rates are lower for people who’ve already tried IVF multiple times but didn’t get pregnant.
- Cause of infertility. Having an average supply of eggs raises your chances of being able to get pregnant using IVF. People who have severe endometriosis are less likely to be able to get pregnant using IVF than are those who have infertility without a clear cause.
- Lifestyle factors. Smoking can lower the chance of success with IVF. Often, people who smoke have fewer eggs retrieved during IVF and may miscarry more often. Obesity also can lower the chances of getting pregnant and having a baby. Use of alcohol, drugs, too much caffeine and certain medicines also can be harmful.
Talk with your care team about any factors that apply to you and how they may affect your chances of a successful pregnancy.
IVF/Fertility Questions and Answers
1 ) What Is The Need For A IVF Treatment For A Couple Suffering With Infertility?
A) Now A Days Due To Many Factors, May Be Ecological, Stress, Genetic Or Couple Problems (Male Or Female Reproductive Organ Problems). So There Is 100% Need To Go For Any Fertility Procedures like IUI, IVF,ICSI, PGS Surrogacy Depending Upon The Above Factors And Age Of Couples. The Couple Can Wait For 1 Year Period For Their Fertility Without Using Any Contraceptives.
2) Is IVF Required For Every Couple Suffering With Fertility Issues?
A) Mostly Females Suffering With Tubal Factors Requires IVF
3) Which Couple Suffering With Infertility Need ICSI Treatment?
A) The Aged Females Who Has Less Ovarian Reserve(Oocytes), PCOS, Endometriosis,, Male Factors Like Oligo, Asthana, Teramo Azoospermia Requires ICSI Treatment.
5) Can IVF Or ICSI Give 100% Success?
A) Can Be/Cannot Be.. 30-40% Couples Get Success With In 1 Cycle, Remaining May Need To Undergo The Procedure Twice Or Thrice.
6 Is Egg Donation Mandatory For Female Over The Age Of 40 Years?
A) No, 100% Depends Upon The Amh Levels And Quantity And Quality Of Oocytes.
7 How Many Times Can A Couple Undergo ICSI Treatment?
A) Maximum 3 Cycles, More Than That Its Couple Choice To Take The Decision For Treatment.
8) Is Surrogacy Treatment Helpful For Couple Suffering With Failed Fertility Procedures?
A) Definitely Best With PGS Procedure.
9) With Recurrent Abortion Patients , Is IVF Helpful?
A) Not Certainly, PGS + IVF May Be Helpful, So That We Can Recognize Genetic Problems Of Embryos And Recurrent Abortion Can Be Prevented.
10) What Exactly Can Be Done In ICSI And Blastocyst Treatment And How Is It Helpful In Fertility Treatment?
A) 1) We Do Hatching Of Oolemma By Passing Laser Beam, Then Selected Live Spermatozoa Is Injected Through The Hole Made In Olekma. There Are More Chances For Good Embryo Formation, Microvilli Like Structure Will Be Formed And Helps In Implantation.
2) Best Procedure Is Oocyte Donation, Sometimes We Can Try By Giving More Injections.
11) Is Oocyte Donation Mandatory For People Having Low Amh Level Below 1.5?
A) Medication For 2-3 Months Can Be Given. Treatment May Be Helpful, But Not In All Cases.
12) Is There Any Possibility To Improve Amh Levels In Infertility Seeking Patients?
A) Definitely
13) What Is The Reason For Infertility Now A Days In Many Couple?
A) Different Job Timings For Couples, Stress Factors In Jobs, Nuclear Families( No Body In Position To Tell What Is Required For Them), Increase Age For Marriage, Junk Foods, Changes In Life Style, Changes In Ecological Factors.
14) Does All Couples Require Fertility Treatment Whose Married Life Is More Than 5 Years?
A) Yes, Quality Of Egg Decreases , Receptive Capacity Of Endometrium Decreases, Male Factors( Decrease Quality And Quantity Of Spermatozoa), Increase In Life Style Disorders(Hypertension, Diabetics)
15) Is Fertility Problems Related To High Age Group Couple?
A) Yes, The Best Treatment For Them Is Surrogacy
16) Is Child Bearing Possible For Patients With Family Planning Surgery?
A) Yes, Possible With 1. Tubal Realization 2.Fertility Procedures Like IVF
17) Is Hypothyroidism And Diabetic Patients Suffer More With Fertility Problems?
A) In Diabetics, Loss Of Libido Is Major Cause For Infertility. PCOS, Irregular Cycles, Hypothyroidism Usually Complements Each Others
18) Patients With Adenomyosis, Grade 3-4 Endometriosis, Multiple Fibroids Must Undergo Surrogacy Procedure?
A) It Is Possible , Try To Contact The Doctor Personally.
19) Can Surrogacy Procedures Give Cent Percent Guaranteed Success?
A) We Can For Best Results In Repeated Cycles.
20) A Female With Uterine Fibroid Suffering With Infertility, What Is The Best Treatment Whether To Remove The Fibroid Or To Undergo Fertility Treatment?
A) If The Size Of Fibroid Is Less Than 5 Cms and If It Is Subseries You Can Go For IVF Procedure. If Fibroid Is Intramural, Endometrial Better To Go For Surgery , Then Try For Fertility Treatment.
21) Can Child Bearing Be Possible With Primary Amenorrhea (Not Attained Menarche Patients)?
A) Now A Days, More Number Of Females Are Facing This Kind Of Problems Due To Many Factors.
22) Is Premature Ovarian Failure Possible At The Age Of 20 Years?
A) Now A Days, More Number Of Females Are Facing This Kind Of Problems Due To Many Factors.
23) What Is The Choice Of Treatment In Young Lady With Premature Ovarian Failure?
A) Oocyte Donation Is The Best Option.
24) Is Egg Freezing Mandatory In Ovarian Cancer Patient Of Young Age Group For Future Fertility? A) Yes It Is Mandatory
25) What Is The Usual Cost Of IVF?
A) Cost Will Be Around 5ok-3l, Depends Upon May Other Factors Like Oocyte Donation, Number And Type Of Injections Given To Female During IVF.
26) Can IUI Procedure Give Success With Male Infertility?
A) It Gives Less Success Rate, In Most Of The Cases IVF Is Helpful In Female Infertilit
27) How Many Times Can A Couple Undergo IUI Procedures?
A) More 5 To 6 Times
28) How Many Months A Couple Seek Fertility Treatment With Normal Medication?
A) Around 6 To 10 Months With Normal Medication
29) Can Mental Stress Affect Child Bearing?
A) Definitely, It Does Affect, Mental Stress Causes Lifestyle Imbalance And Hormonal Imbalance
30) Why Software Couples Are Suffering With Problems Of Infertility?
A) May Be The Effects Of Laptop, Target Stress, Shift Work Sleep Disorder, Unhealthy Eating Habits
31) Will Life Style And Fast Food Affects One’s Fertility?
A) Definitely
32) Does Female Education And Hard Work Is The Reason For More Fertility Problems Now- A- Days?
A) Yes, 100% Because Of Reduction In Oocyte Quantity And Quality Due To Increase In Age Of Marriage And Conception And Reduction In Implantation Of Embryo’s In Endometrial Cavity
33) What Is The Reason For Ovarian Failure In Many Women Seeking Fertility?
A) Prolonged Exposure To Pesticides, And Other Toxins, Which Are Used Frequently, Autoimmune Disorders Like Rheumatoid Arthritis, Thyroid Disorders. And Genetic Disorders Like Chromosomal Disorders, Fragile X Syndrome And Iatrogenic Causes Like Chemotherapy And Radiotherapy. Non Identifiable, Ecology Or Etiology Can Be Reason For Premature Menopause And Oocyte Reduction In Ovaries
34) Reason For Irregular Periods In Young generation Now A Days?
A) Because Of Education And Professional Stress, Girl May Be Something Going On With Her, Excessive Exercise, Not Eating Enough Calories, Being Underweight Or Overweight Can Effect A Girl Cycle
35) Is PCOS Curable?
A) Yes, It Is Curable
36) What Could Be The Reason For Hormonal Imbalance Which Causes Infertility In Young Couples?
A) Getting Irregular Periods, Breast Milk Agalactorrhea, Thyroid Related Disorders, Increase In Body Weight, Increase In Alteration In Ovarian Hormones Can Cause Infertility?
37) What Is Reason For Repeated Abortion?
A) Most Probably Genetic Disorders( Single Gene Defects Or Gene Mutation), Hormone Related Disorders (Thyroid), Immunological Disorders(Sle) And Few Idiopathic
38) What Is The Reason For IVF Failure?
A) Decrease Quality Of Oocytes In Females, Quality Of Sperm In Male, Quality Of Embryo After Fertilization, Known And Unknown Disorders Of Endometrial Cavity
39) Is Repeated IVF Is Mandatory For Getting Good Results?
A) The Receiving Capacity Of Endometrium Increases With Repeated Embryo Transfer.
40) Is Chocolate Cyst Reason For Infertility?
A) The Oocyte Quality Will Decrease In Endometrium Or In Chocolate Cyst, Fertilization Capacity In The Tubes Will Decrease.
41) What Is Implantation Failure?
A) Some Disorders Like Genetic Abnormalities Where Embryo With Good Morphology Having Aneuploidy, Hormonal Or Metabolic Disorders ( Uncontrollable Diabetics), Infection Causes Implantation Failure
42) Is There Chances Of Abortion After Fertility Treatment?
A) Yes There Are Chances Of Abortion After Fertility Treatment Like Normal Conceptions
43) Is Laparoscopy Or Hysteroscopy Require Before Patients Undergoing Fertility Treatment?
A) Yes Definitely To Analyze The Anatomical Or Pathological Defects In Reproductive Organs Like Uterus, Tubes, Ovaraies, Tubo Ovarian Relations, Polyps, Mucosal Disorders. Uterine Septum And Blood Supply
44) How Many Months A Women Can Wait After Laparoscopy Procedure To Conceive?
A) Up To 6 Months
45) Why Hysteroscopy Procedure Done Before IVF Procedure?
A) To Know About Uterine Cavity, Mucosal Capacity, Blood supply To Rule Out Pathological Defects Like Mild Syncheia, Polyps Etc
46) After Resection Of Uterine Septum, How Many Months Can A Women Wait For Successful Pregnancy?
A) up to 6 Months To 1 Year
47) After Tubal Repairing Procedure Through Laparoscopy With In How Many Months A Women Can Conceive, If Not What Can Be Done?
A) With In 6 Months Of Time, If Not Immediately Consult A Good Infertility Specialist
48) Why Corneal End Of Tube To Be Closed In Cases Of Pyo Or Hemato Salpinx?
A) After Embryo Transfer, Tubal Fluid May Washout Embryos, If The Corneal End Of Tube Is Open
49) Can A Women With Bicorn ate Uterus Conceive Easily Or Requires Treatment?
A) Few People Will Conceive But It May Cause Premature Birth. A Good Gynecologist Care Is Must During Pregnancy
50) What Will Happen In Infertile Unicorn ate Uterus People, Whether Treatment Is Necessary?
A) There May Go For 2nd Trimester Abortions, Premature Birth Due To Small Size Of Uterus, Sometimes Decrease In Implantation Capacity.